What Are Preventive Health Care Services Things To Know Before You Buy
Crumpler was born complimentary and skilled and practiced in Boston. At the close of the war, she signed up with the Freedmen's Bureau and worked in the freed individuals's communities of Virginia. In 1883, she released one of the first treatises on the burden of disease in black communities. "They seem to forget there is a cause for each ailment," she composed.
That bloc maintained the country's racial stratification by securing regional control of federal programs under a mantra of "states' rights" and, in many cases, by adding qualifications straight to federal laws with inequitable intent. As the Columbia University historian Individual retirement account Katznelson and others have actually recorded, it was mainly at the request of Southern Democrats that farm and domestic employees over half the nation's black labor force at the time were left out from New Deal policies, consisting of the Social Security and Wagner Acts of 1935 (the Wagner Act guaranteed the right of workers to cumulative bargaining), and the Fair Labor Standards Act http://edgarxxre507.raidersfanteamshop.com/some-known-factual-statements-about-what-services-are-provided-in-acute-care-behavioral-health-units of 1938, which set a minimum wage and developed the eight-hour workday.
Bill, allowing state leaders to successfully exclude black individuals. [Myths about physical racial distinctions were used to validate slavery and are still thought by doctors today.] In 1945, when President Truman contacted Congress to expand the nation's healthcare facility system as part of a bigger health care strategy, Southern Democrats obtained key concessions that formed the American medical landscape for years to come.
However it also made sure that states managed the dispensation of funds and might segregate resulting centers. Professional societies like the American Medical Association barred black physicians; medical schools left out black students, and the majority of health centers and health clinics segregated black clients. Federal health care policy was created, both implicitly and clearly, to omit black Americans.
10 Simple Techniques For What Is Primary Health Care
What's more, access to good medical care was asserted on a system of employer-based insurance that was naturally difficult for black Americans to get. "They were denied most of the jobs that offered protection," says David Barton Smith, an emeritus historian of health care policy at Temple University. "And even when a few of them got health insurance coverage, as the Pullman Addiction Treatment Delray porters did, they could not utilize white centers." In the shadows of this exemption, black neighborhoods produced their own health systems.
Black medical professionals and nurses most of them trained at one of 2 black medical colleges, Meharry and Howard developed their own expert organizations and began a collective war against medical apartheid. By the 1950s, they were pushing for a federal healthcare system for all citizens. [To get updates on The 1619 Project, and for more on race from The New York Times, our weekly Race/Related newsletter.] That battle put the National Medical Association (the leading black medical society) into direct conflict with the A.M.A., which was opposed to any nationalized health plan.
The group used the same arguments in the mid- '60s, when supporters of nationwide medical insurance introduced Medicare. This time, the N.M.A. developed a countermessage: Health care was a fundamental human right. Medicare and Medicaid became part of a broader strategy that finally brought the legal partition of medical facilities to an end: The 1964 Civil liberty Act forbade segregation for any entity receiving federal funds, and the brand-new health care programs soon placed every medical facility in the nation in that category.
Those who did not fit into specific age, work or income groups had little to no access to health care. Budget friendly Care Act brought health insurance to almost 20 million previously uninsured grownups. The biggest recipients of this benefit were people of color, many of whom acquired protection through the law's Medicaid growth.
Indicators on When Does Senate Vote On Health Care Bill You Need To Know
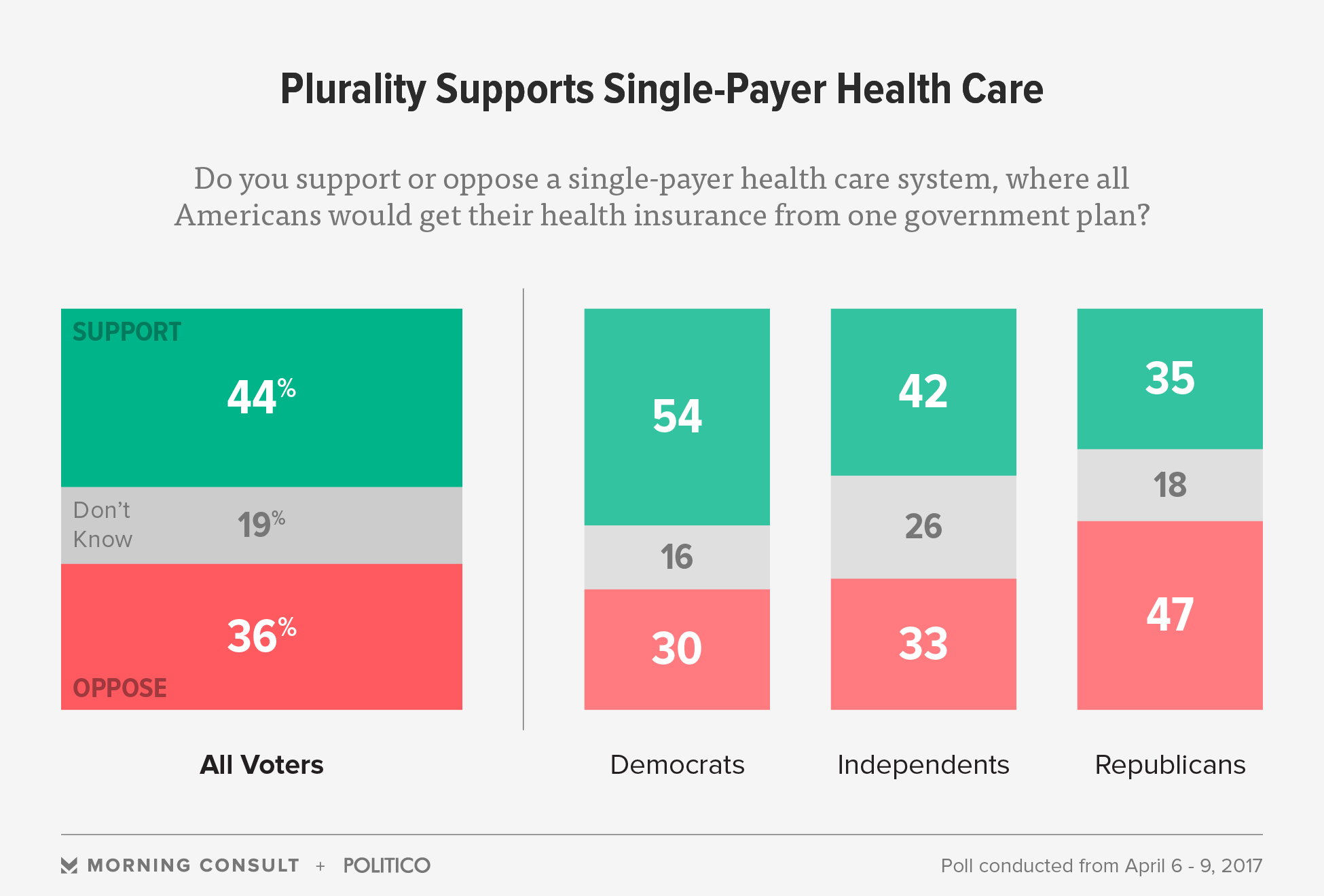
A number of states, most of them in the previous Confederacy, refused to participate in Medicaid expansion. And a number of are still attempting to make access to the program contingent on difficult new work requirements. The results of both policies have been indisputable. States that broadened Medicaid saw a drop in disease-related deaths, according to the National Bureau of Economic Research.
One hundred and fifty years after the freed individuals of the South very first petitioned the federal government for standard medical care, the United States stays the only high-income nation on the planet where such care is not ensured to every person. In the United States, racial health disparities have proved as fundamental as democracy itself.
" Disparity is developed into the system." Medicare, Medicaid and the Affordable Care Act have actually helped diminish those variations. However no federal health policy yet has eradicated them (how much does medicare pay for home health care per hour).
By Rosana G. Ferraro It's that time of year again when insurance provider ask for medical insurance rate increases [] By: Rosana Ferraro Wondering what took place in the unique session? We have actually got your back. As you might understand, lawmakers got [] By Jackie Nappo and Jill Zorn Recently, Universal Health Care has actually been discussing diverse health outcomes, particularly as [].
How Much Would Universal Health Care Cost Can Be Fun For Anyone
All over I went last fall, I would typically hear the same twang of pitywhen I informed someone I 'd come to their country from America to learn how their health care works. There were 3 minutes I will always keep in mind, one from each of my trips to Taiwan, Australia, and the Netherlands.
I was walking along a township road, plainly out of place, and he was planting Click here to find out more orchids with his mom. He stopped me and asked what I was doing there. I said I was a journalist from the US, reporting on healthcare. He smiled a bit and then went directly into a story, about his good friend who was living in Los Angeles and broke his arm however returned to Taiwan to get it repaired due to the fact that it 'd be more affordable than getting it repaired in the United States.
We nestled in a little building with a coffee shop and traveler details desk, and one of the workers, Mike, introduced himself. I ended up telling him why we existed; he considered it a moment and then stated: Well, we have actually got some problems, but absolutely nothing as bad as yours.
Our project was enabled by a grant from.) In the Netherlands, the researchers I consulted with at Radboud University had actually asked me to give a presentation on American health care, a quid pro quo for their presentation on the nation's after-hours care program. So I required. There were two minutes when the audience audibly gasped: one when I discussed the number of people in the United States are uninsured and another when I pointed out how much Americans have to invest out of pocket to meet their deductible.
The Ultimate Guide To A Health Care Professional Is Caring For A Patient Who Is About To Begin Taking Isoniazid
People have typically asked which system was my favorite and which one would work best in the US. Alas, that is not so basic a concern to address. However there were certainly plenty of lessons we can heed as our nation participates in its own discussion of the future of healthcare.
Every one of the nations we covered Taiwan, Australia, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom has actually made such a commitment. In fact, every other country in the developed world has actually chosen that health care is something everyone should have access to and that the government should play a substantial function in guaranteeing it. how does the health care tax credit affect my tax return.
